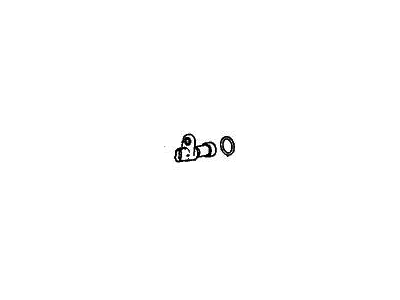×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Acura Parts
- Acura Accessories

My Garage
My Account
Cart
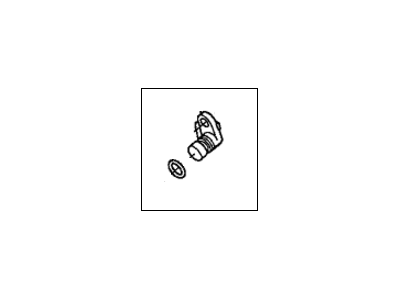
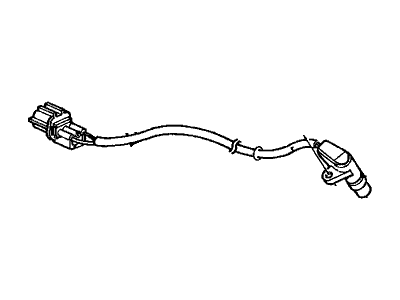
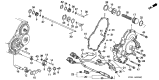
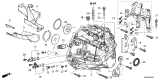
Genuine Acura Integra Speed Sensor
Speed Control Sensor- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
11 Speed Sensors found

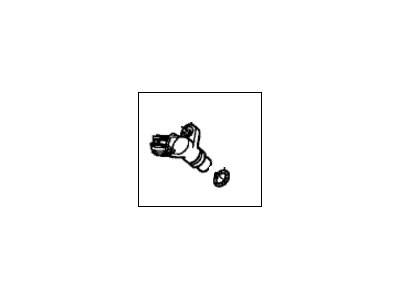
Acura Integra Pick-Up Assembly
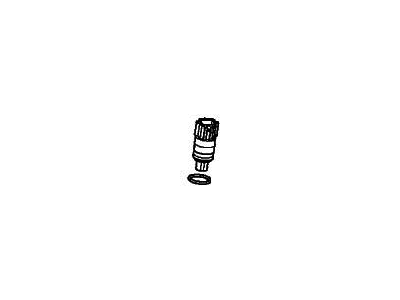
Part Number: 28820-RPC-013$30.03 MSRP: $41.88You Save: $11.85 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysAcura Integra Vehicle Speed Sensor (Denso)
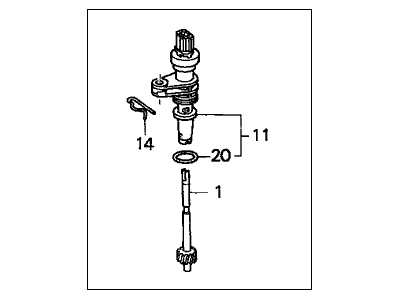
Part Number: 78410-S04-951$201.95 MSRP: $288.42You Save: $86.47 (30%)Ships in 1 Business DayAcura Integra Main Pick-Up Assembly (Denso)
Part Number: 28810-P4R-003$187.44 MSRP: $267.70You Save: $80.26 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysAcura Integra Main Pick-Up Assembly (Tec)
Part Number: 28810-P78-003$222.02 MSRP: $317.08You Save: $95.06 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysAcura Integra Main Pick-Up Assembly (Tec)
Part Number: 28810-P4V-003$187.44 MSRP: $267.70You Save: $80.26 (30%)Ships in 1 Business DayAcura Integra Pick-Up Assembly
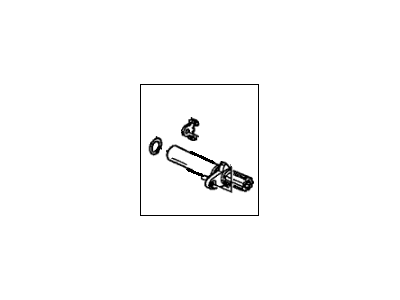
Part Number: 28820-RJ2-003$34.28 MSRP: $47.82You Save: $13.54 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysAcura Integra Pick-Up Assembly
Part Number: 28810-5RG-004$30.97 MSRP: $43.20You Save: $12.23 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Acura Integra Speed Sensor
We provide a broad range of OEM Acura Integra Speed Sensor at unbeatable prices on our website. For your OEM parts, You can count on the guaranteed quality, manufacturer's warranty, outstanding customer service, and prompt delivery. We look forward to your visit.
Acura Integra Speed Sensor Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: How does the Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) function and how can it be tested on Acura Integra?A:The Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS), located on the transaxle, is a permanent magnetic variable reluctance sensor that generates a pulsing voltage when the vehicle speed exceeds 3 mph, with these pulses utilized by the PCM to manage fuel injector duration and transaxle shift control. To check the VSS, disconnect the electrical connector in the wiring harness at the sensor and use a voltmeter to measure voltage at the connector; the circuit should have battery voltage available. If no voltage is present, inspect for an open circuit between the VSS and the fuse box, and check the black wire of the connector for continuity to body ground using an ohmmeter. If continuity is absent, look for breaks or poor connections in the black wire. To test the sensor, raise the front of the vehicle securely on jackstands, block the rear wheels, and place the transaxle in Neutral. After connecting the electrical connector to the VSS and turning the ignition to On, backprobe the VSS connector signal wire with a voltmeter, connecting the negative lead to body ground. While holding one wheel steady, rotate the other wheel by hand; the voltmeter should pulse between zero and 5 volts, indicating the sensor is functioning properly. If it does not pulse, the sensor should be replaced by disconnecting the electrical connector, removing the retaining bolt, and lifting the VSS from the transaxle, with installation following the reverse order of removal.